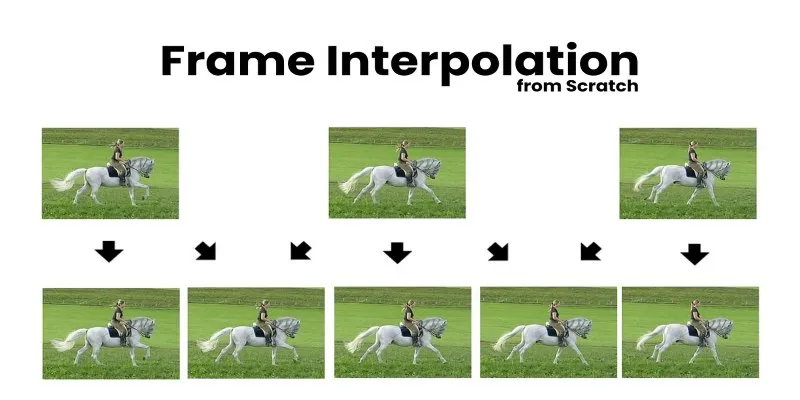
Boost Video Quality with AI: A Complete Guide to Frame Interpolation
If you've ever watched a choppy video and wished it could be smoother, you’ve already thought about the magic of frame interpolation—whether you knew it or not. Frame interpolation is a technique that enhances video fluidity by generating new frames between existing ones. It’s widely used in animation, gaming, and video editing, making movements appear more seamless and realistic. The process, once reserved for professionals, is now more accessible than ever, thanks to AI and machine learning advancements.
The idea is simple but revolutionary: instead of accepting a video's natural frame rate, frame interpolation artificially boosts it, reducing stutter and lag. With AI-powered tools, it's even possible to generate entirely new frames that blend naturally with the surrounding ones. Whether you're a casual viewer or a content creator, understanding frame interpolation can change how you experience and produce videos.
How Frame Interpolation Works
At a fundamental level, frame interpolation examines the movement between two available frames and estimates what an in-between frame would appear like. Older interpolation techniques rely on mathematical equations to calculate this movement, whereas new AI-based approaches are more sophisticated in that they learn patterns from enormous video datasets.
One of the first frame interpolation methods used linear techniques, where the system would grab two frames and merge them by averaging their pixel values. While this would remove small movements, it tended to create ghosting artifacts or abnormally blurred objects. Later and more sophisticated techniques, such as motion vector analysis, observe how objects translate from one frame to another so that more precise in-between frame creation can be achieved.
AI has transformed frame interpolation. Rather than depending solely on motion estimation, AI-based algorithms learn from huge video datasets to anticipate how motion would typically progress. This has given rise to deep learning-based interpolation software that can generate realistic, artifact-free frames with high accuracy.
Applications of Frame Interpolation
Video Playback Enhancement
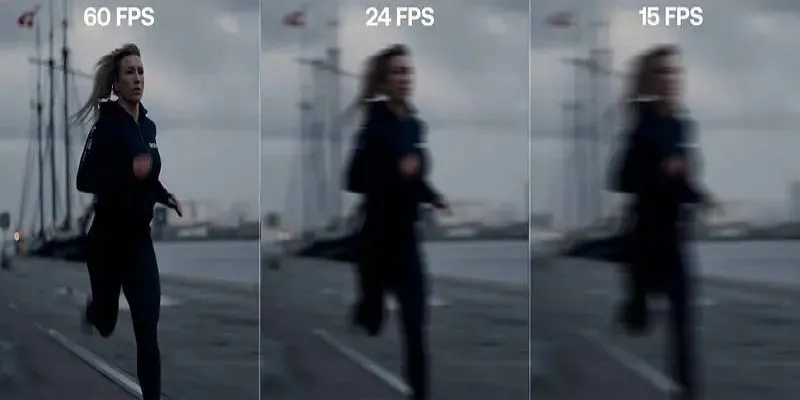

Frame interpolation is one of the most widely used applications of this technique in video display. It's most regularly utilized in contemporary televisions, online streaming services, and other video display units that try to offer a smoother experience. Content with lower frame rates, like older movies or videos recorded at a frame rate of 30 fps, may appear jerky while displayed on a high-refresh-rate display. Frame interpolation comes in here and adds extra frames to increase the frame rate of the video, yielding more smooth and fluid movement.
For example, while you are viewing sports, particularly rapid sports like basketball or football, interpolated frames diminish the stuttering effect commonly encountered in camera rapid motion. With action smoothened out, there is greater clarity. Hence, the experience makes the content look more real and immersive.
Gaming
The gaming industry has also embraced frame interpolation, particularly in cases where users have hardware limitations. Many gamers, especially those using older or budget-friendly systems, struggle to maintain a stable frame rate when playing graphically demanding games. Frame interpolation helps solve this problem by adding intermediate frames in real time, giving the illusion of a higher frame rate.
This process can make games appear smoother, even on machines that would otherwise struggle with high-end graphics. Some software solutions powered by AI use interpolation to give users the experience of 60 fps or higher without needing to upgrade their hardware.
Animation
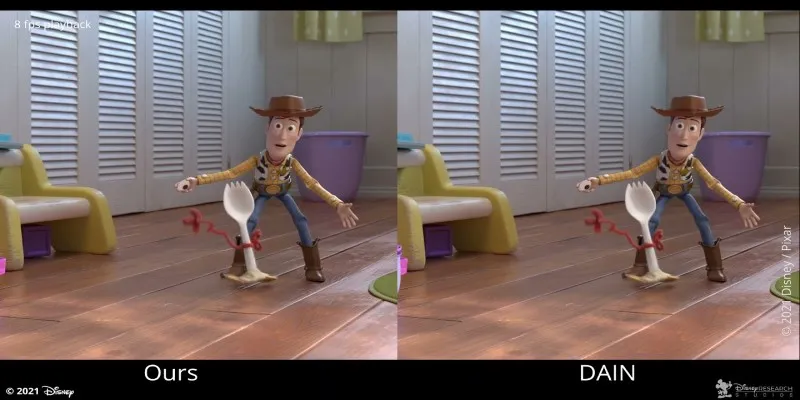

In the world of animation, frame interpolation has simplified the production process significantly. Instead of animators having to hand-draw or manually render every single frame, they can now create keyframes—those crucial frames that define major transitions—and let interpolation software fill in the gaps.
This saves immense time and effort while maintaining smooth, fluid motion. It also allows studios to allocate resources more efficiently, ensuring that animators can focus on more creative tasks while leaving the technical interpolation work to AI tools. The result is faster production cycles, allowing for higher output in less time without sacrificing visual quality.
Historical Footage Restoration
Another fascinating application of frame interpolation is in the restoration of historical footage. Many old films were shot at lower frame rates, sometimes as low as 16 fps. When viewed on modern devices, these films appear jumpy and distorted due to the disparity between their original frame rate and the high frame rate of contemporary screens.
However, using frame interpolation, these old films can be upscaled to meet modern standards. By generating additional frames based on the motion patterns of the original footage, interpolation software smooths out the viewing experience, breathing new life into vintage films.
Advantages and Limitations
Frame interpolation offers several benefits, but it’s not without its downsides. Understanding both sides of the equation helps users make informed choices about when and how to use it.
One of the biggest advantages is improved smoothness. Whether it’s a video, game, or animation, interpolating frames results in a more fluid experience. This is particularly noticeable in high-action sequences where stuttering can break immersion. The ability to upscale lower frame-rate content without re-recording or re-rendering also saves significant time and resources.
Another benefit is accessibility. AI-powered frame interpolation has become easier to use, with various software options offering simple implementations. You don’t need to be a professional editor or animator to take advantage of this technology—many tools provide automated interpolation with just a few clicks.
However, frame interpolation isn't perfect. One of the main issues is motion artifacts, where incorrectly predicted frames can create distortions, ghosting, or unnatural warping. This can be especially problematic in complex scenes with rapid or unpredictable movement. AI has reduced this issue, but it hasn't eliminated it.
Additionally, while frame interpolation improves perceived smoothness, it doesn’t add actual detail. A low-resolution, low-quality video will still look subpar even if it’s interpolated to a higher frame rate. Some purists also argue that interpolation removes the "cinematic feel" of certain content, especially in movies shot at 24 frames per second.
Conclusion
Frame interpolation revolutionizes video quality for enthusiasts, gamers, animators, and filmmakers. Generating intermediate frames turns choppy, low-frame-rate footage into smooth visuals. Thanks to AI advancements, this process is more accurate and accessible than ever, even for casual users. While there are some drawbacks, such as motion artifacts and concerns about cinematic authenticity, the advantages often outweigh the limitations. Whether restoring old footage, enhancing gaming performance, or improving animations, frame interpolation enhances visual experiences. As AI evolves, we can expect even more refined and lifelike interpolations, taking video quality to new heights.
Related Articles

How to Use Browse AI to Scrape Data from Any Website: A Step-by-Step Guide

Which Are The 5 Best Pomodoro Timer Apps to Boost Your Productivity in 2025

The Basics of S and OP: A Beginner’s Guide to Sales and Operations Planning
Boost Video Quality with AI: A Complete Guide to Frame Interpolation
Improve Your Videos with These Top 4 Free AI Video Enhancers

How to Push Code to GitHub: A Step-by-Step Guide

Record Your Screen: 10 Best GIF Creator Tools

Upgrade Your Streaming: 5 Chrome Extensions to Enhance Video Quality

How to Effortlessly Combine MP4 Videos on Your Desktop

Best Methods to Convert MKV to WAV Without Audio Quality Loss

Descript Not Enough? Try These 5 Powerful Editing Alternatives

 bobobk
bobobk